The Blueprint for Startup Financial Success
In the dynamic world of startups, financial modeling is more than a spreadsheet exercise; it is a strategic compass that guides growth, scalability, and sustainability. Many entrepreneurs focus heavily on product development or service differentiation, neglecting the financial infrastructure that powers their operations. A robust financial model not only outlines how a startup intends to generate revenue but also ensures that every aspect of the customer journey, from acquisition to retention, aligns with long-term profitability.
This whitepaper explores the essential components of a successful startup financial model, beginning with strategies for customer acquisition and culminating in a sustainable revenue generation framework. It provides actionable insights for entrepreneurs, investors, and financial strategists looking to build a comprehensive, data-driven financial roadmap that aligns with market realities. By covering key metrics, customer acquisition cost (CAC), lifetime value (LTV), pricing strategies, and revenue projections, this whitepaper serves as a step-by-step guide to financial modeling excellence.
Understanding the Startup Financial Model
Defining Financial Modeling for Startups
A financial model is the foundation upon which every successful startup builds its strategic decisions. Unlike mature companies, startups operate in an environment of high uncertainty, which makes dynamic and adaptable financial modeling critical. This model is not merely a prediction tool; it reflects the company’s core assumptions about its operations, market size, and revenue streams.
A strong financial model integrates both quantitative and qualitative elements. It combines market data, user behavior, and competitive benchmarks with the startup’s internal metrics. From there, it generates insights into cash flow, profitability, and break-even points, ensuring founders can articulate a clear vision for their business’s financial health.
The Role of Customer Acquisition in Financial Success
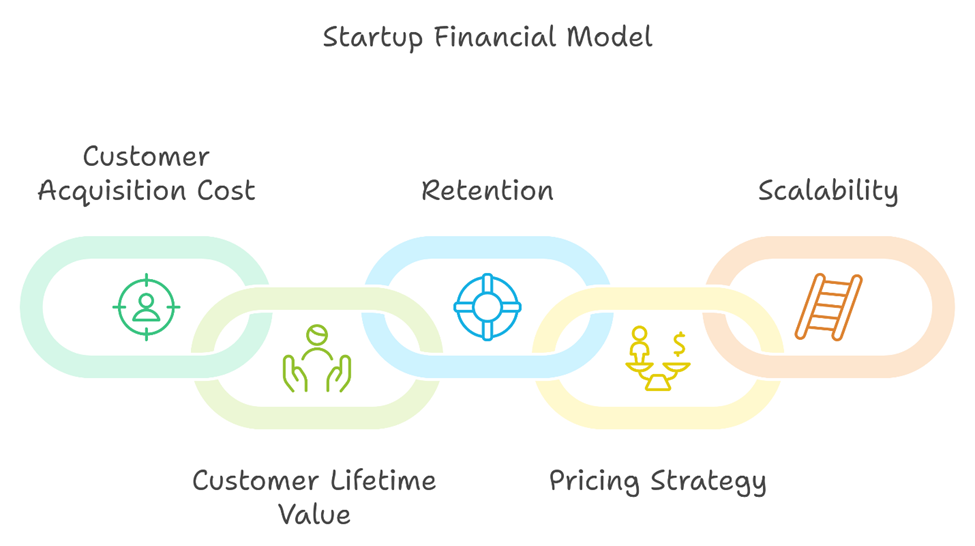
Customer acquisition is the first step in the startup journey toward revenue generation. However, without a clear understanding of the costs and returns associated with acquiring customers, startups risk burning through capital without achieving sustainable growth. The interplay between CAC and LTV is a critical determinant of a startup’s financial viability. A successful financial model incorporates these metrics, allowing founders to make data-driven decisions about marketing budgets, sales strategies, and customer retention initiatives.
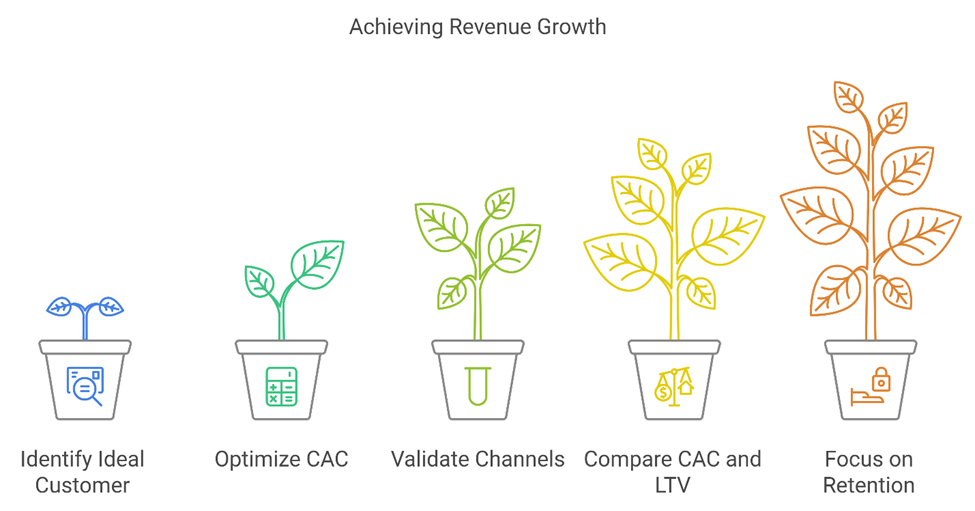
The Customer Acquisition Journey: Metrics and Strategies
Identifying and Targeting Your Ideal Customer
The journey toward revenue begins with identifying the ideal customer. This step involves understanding the market segmentation, customer personas, and pain points that your product or service addresses. A financial model must integrate customer segmentation data, using assumptions grounded in market research and competitive analysis.
By focusing on high-value customers, startups can optimize their CAC. Early-stage companies should validate acquisition channels through experimentation, refining their strategies to ensure every dollar spent generates measurable results.
Calculating Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
CAC is a cornerstone of any startup’s financial model. It includes all costs associated with acquiring a customer, such as marketing expenses, sales team salaries, and technology tools. To calculate CAC effectively, startups need granular tracking of their spending across various channels, from digital advertising to direct sales efforts.
Accurate CAC data empowers startups to make informed decisions about their growth strategies. For instance, it highlights whether to double down on a high-performing channel or pivot away from a low-ROI initiative. Furthermore, startups must compare their CAC against their LTV to ensure that each customer generates more revenue than the cost to acquire them.
The Role of Retention in Revenue Growth
Customer acquisition is only part of the equation. Retention is equally, if not more, important to sustainable financial success. A robust financial model accounts for churn rates, upselling opportunities, and recurring revenue streams. These elements not only improve LTV but also stabilize revenue projections, making the startup more attractive to investors.
Revenue Generation Strategies for Startups
Crafting a Scalable Pricing Model
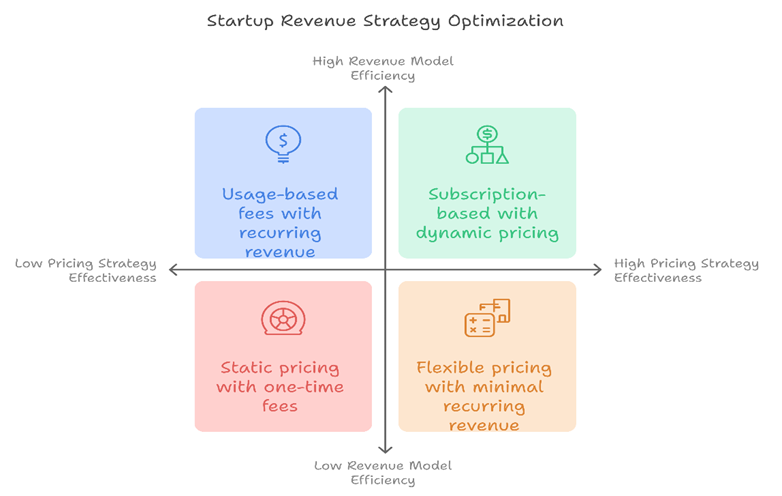
The transition from customer acquisition to revenue generation hinges on a well-defined pricing strategy. Startups must evaluate their market position, value proposition, and customer willingness to pay. A pricing model should reflect the perceived value of the product or service while leaving room for scalability.
Dynamic pricing models, such as subscription tiers or usage-based fees, can help startups maximize revenue across diverse customer segments. In addition, the financial model should include sensitivity analyses to assess how pricing changes affect overall revenue and profitability.
Leveraging Recurring Revenue Models
Recurring revenue is the lifeblood of many successful startups. Subscription-based models, in particular, provide predictable income streams and higher customer LTV. Startups should incorporate these models into their financial framework, ensuring that they accurately reflect churn rates and renewal probabilities.
To optimize recurring revenue, startups must invest in customer success initiatives. Happy customers are more likely to renew subscriptions, reducing churn and increasing the predictability of cash flow. This, in turn, improves investor confidence and reduces the need for frequent fundraising.
Forecasting Revenue Growth and Scalability
Revenue forecasting is a delicate balance of optimism and realism. Startups must project their revenue growth based on historical data, market trends, and the scalability of their operations. A robust financial model includes multiple scenarios, ranging from conservative to aggressive, allowing founders to stress-test their assumptions.
By integrating data from customer acquisition, retention, and pricing strategies, startups can create a comprehensive revenue forecast. This forecast not only guides internal decision-making but also serves as a critical tool during investor pitches, demonstrating the startup’s growth potential and financial discipline.
Aligning Financial Models with Business Goals
The Interplay of Metrics and Milestones
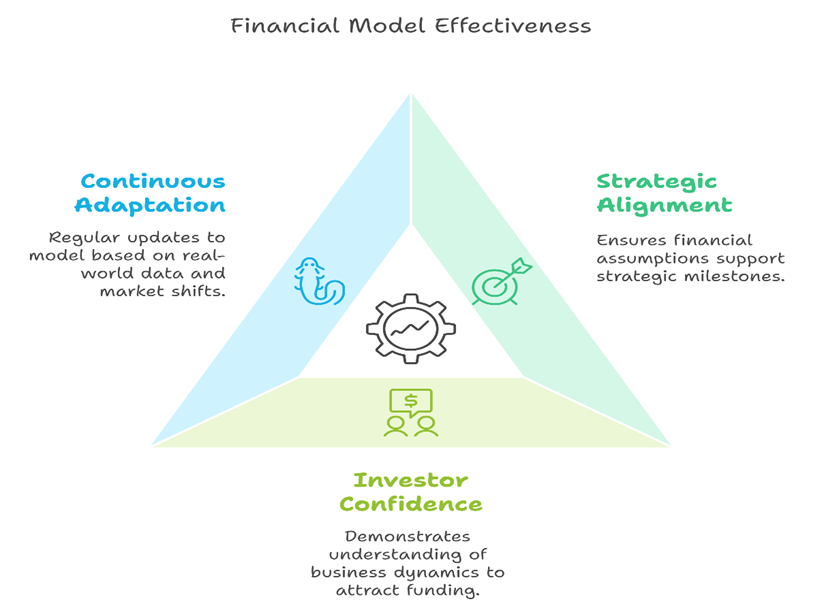
A startup’s financial model is most effective when aligned with its broader business goals. Founders must ensure that their financial assumptions support their strategic milestones, whether it’s entering a new market, launching a product feature, or achieving profitability. This alignment ensures that resources are allocated effectively and that financial projections are both realistic and ambitious.
Building Investor Confidence
For startups seeking external funding, a robust financial model is a non-negotiable asset. It demonstrates that the founders understand their business dynamics and are prepared for the challenges ahead. Startups should be transparent about their assumptions and prepared to adjust them based on investor feedback or market conditions.
Continuous Refinement and Adaptation
The startup journey is inherently unpredictable, and financial models must adapt to changing circumstances. Regular updates to the model, informed by real-world data and shifting market conditions, ensure its relevance and accuracy. Startups that treat their financial models as living documents are better equipped to navigate uncertainty and seize new opportunities.
Building a Financial Model for Long-Term Success
A startup’s financial model is more than a tool for tracking numbers; it is a strategic asset that drives decision-making and inspires investor confidence. By focusing on the customer journey from acquisition to revenue generation, startups can create a financial framework that supports sustainable growth and profitability. This whitepaper has outlined the critical elements of a successful financial model, emphasizing the importance of CAC, LTV, retention, pricing, and scalability.
Entrepreneurs who invest time and effort into building a comprehensive financial model are better positioned to navigate the complexities of the startup ecosystem. Armed with this knowledge, founders can turn their vision into reality, ensuring their startups not only survive but thrive in an increasingly competitive marketplace.





Add comment